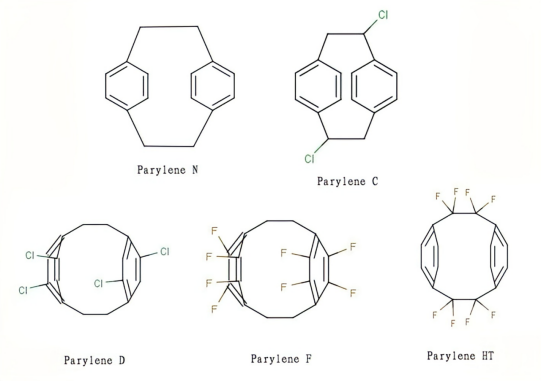
Parylene is a new type of conformal coating material developed and applied by Union Carbide Co. of the United States in the mid-1960s. It is a polymer of para-xylene. According to the differences in molecular structure, Parylene can be divided into various types such as type N, type C, type D, type F, and type HT.
Parylene is a protective polymer material. It can be deposited by vapor phase in a vacuum. The good penetration ability of Parylene active molecules can form a pinhole-free, uniform-thickness transparent insulating coating inside, at the bottom, and around the components, providing a complete and high-quality protective coating for the components to resist the erosion of acids, alkalis, salt spray, mold and various corrosive gases. Since Parylene is not a liquid, there will be no accumulation, bridging or meniscus formation during the coating process.

Why is Parylene Coated on NdFeB Permanent Magnets?
NdFeB permanent magnet material is a high-performance and strong magnetic material, but it is very unstable in the air. Larger-sized ones are usually coated with electroplating or epoxy electrophoretic paint as protective coatings. For smaller-sized magnetic materials, especially ring-shaped and cylindrical magnetic materials, it is difficult to meet the application requirements with the above traditional protection methods. The combination of Parylene's unique preparation process and excellent performance enables it to fully coat small and ultra-small magnetic materials without weak points. The magnetic materials can be immersed in hydrochloric acid for more than 10 days without corrosion. At present, many small and ultra-small magnetic materials in the world use Parylene as insulation and protective coating.

Preparation and Polymerization Process of Parylene Films
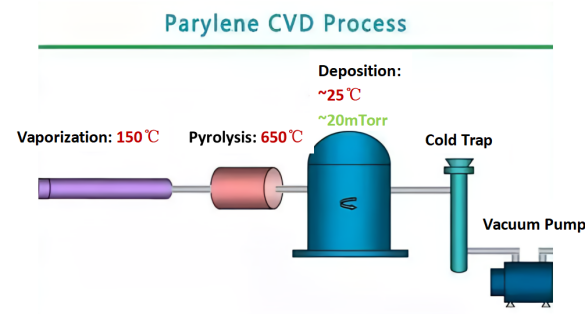
The commonly used method for preparing Parylene is Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD), which is a process technology in which reactants undergo spatial gas-phase chemical reactions in a gaseous state to directly generate solid substances on the surface of solid substrates, and then form a coating on the surface of the substrate.
The preparation process of Parylene films is divided into three steps: vaporization of monomers, pyrolysis, and adhesion and deposition on the substrate surface.
1. In a vacuum environment, solid para-xylylene cyclic dimer sublimes into a gaseous state at about 150℃.
2. At about 650℃, the para-xylylene cyclic dimer cracks into free radical-containing active 2,5-dichloro-para-xylylene.
3. At room temperature (25℃), the free 2,5-dichloro-para-xylylene deposits and polymerizes on the surface of the solid substrate to form a pinhole-free conformal film.

Protective Effects of Parylene Coating
1. Resistance to Acid and Alkali Corrosion: It can solve the problem of corrosion by acidic or alkaline substances.
2. Low Water and Gas Permeability with High Barrier Effect: It can achieve moisture resistance, water resistance, rust prevention and slow down weathering.
3. Resistance to Organic Solvent: It is insoluble in common solvents.
4. Colorless and High Transparency: The film layer does not affect the original appearance of the product.
5. Dust, Moisture and Water Resistance with Breathability: It can make the product meet the international IP rating standards for dust and water resistance.