Processes
Combination of proprietary technology and modern production techniques
01

Preparation of raw materials according to recipe ratios
02
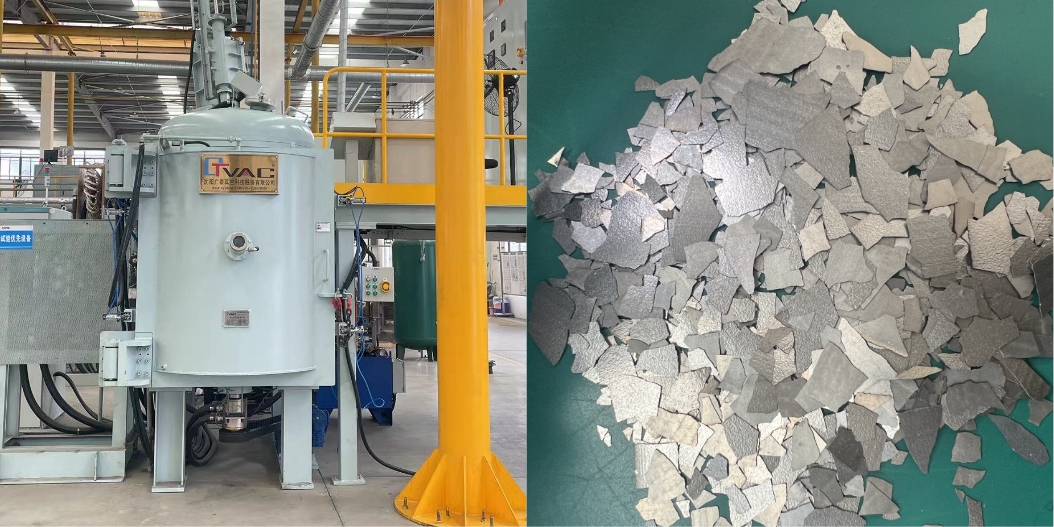

Melting and flaking
03
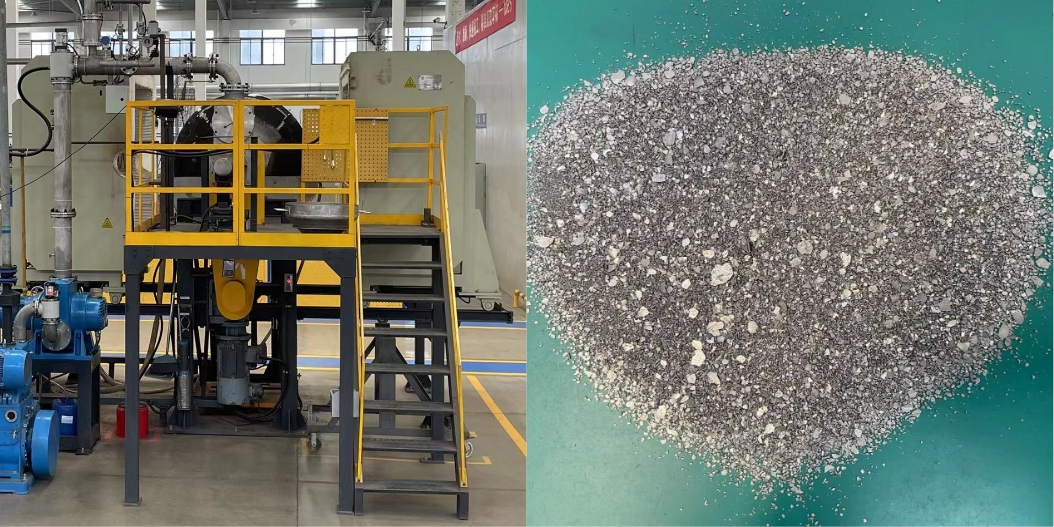

Hydrogen crushing and air flow milling
04
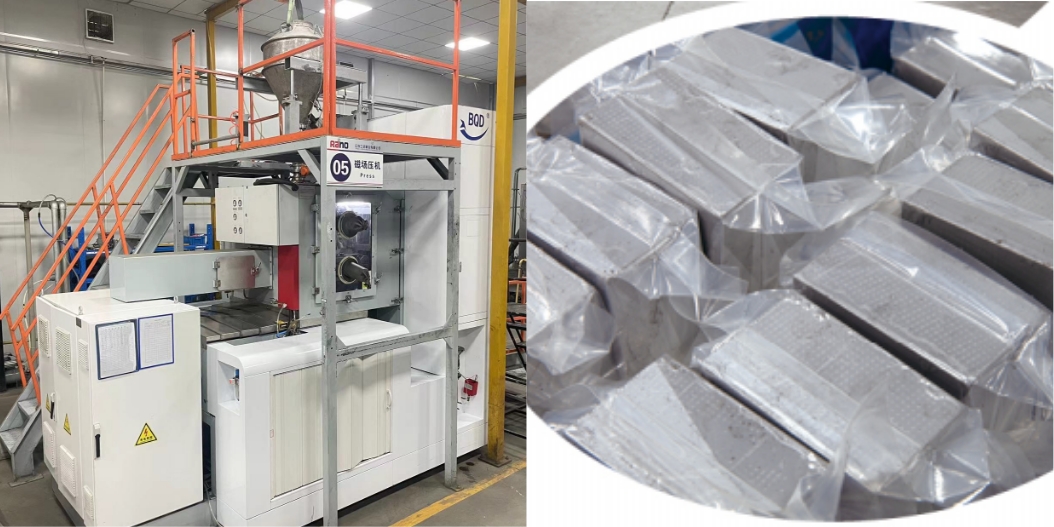

Blank Forming and Orientation in Magnetic Fields
05
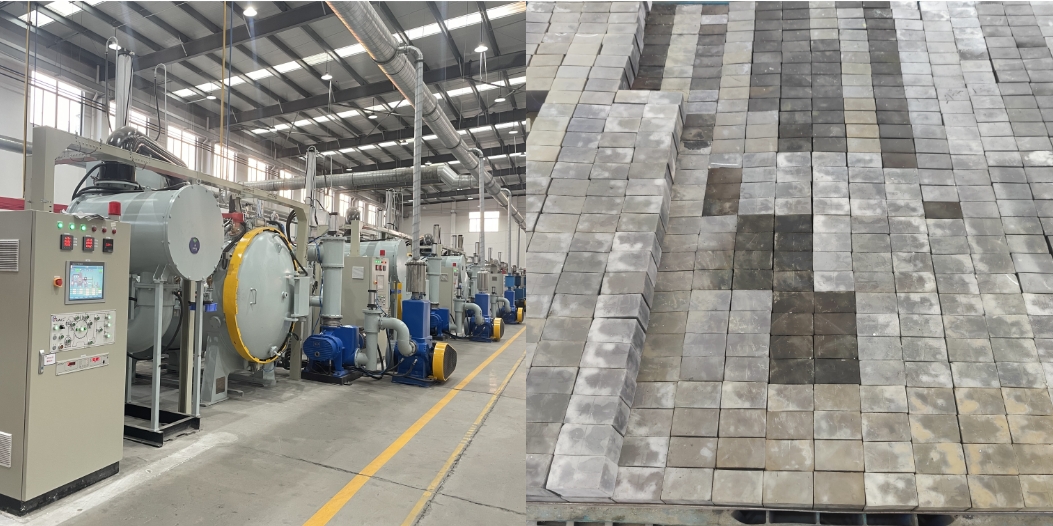

Sintering & Ageing
06
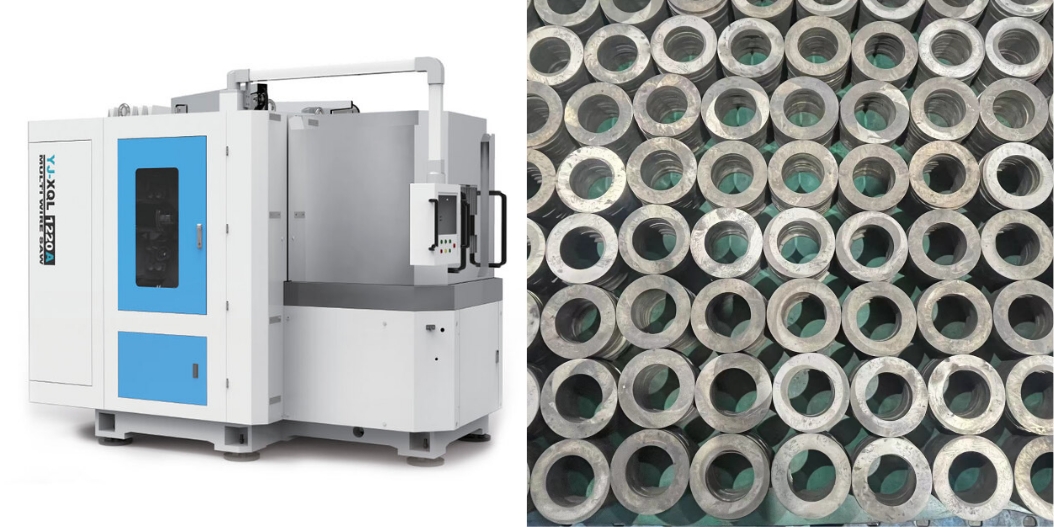

Machining
07

Electroplated
08

Product saturation magnetization
09

Packaging and transportation
IQC
Analyze alloy structure and composition
Examining particle size and particle size distribution
Checking the dimensions and perpendicularity of the blank
Detection of sintered dimensions and magnetic properties
Inspection of dimensional accuracy
Detecting Flux
Inspection of appearance, etc.
Packaging and transportation
Processes
01

Preparation of raw materials according to recipe ratios
IQC
02

Melting and flaking
Analyze alloy structure and composition
03

Hydrogen crushing and air flow milling
Examining particle size and particle size distribution
04

Blank Forming and Orientation in Magnetic Fields
Checking the dimensions and perpendicularity of the blank
05

Sintering & Ageing
Detection of sintered dimensions and magnetic properties
06

Machining
Inspection of dimensional accuracy
07

Electroplated
Detecting Flux
08

Product saturation magnetization
Inspection of appearance, etc.
09

Packaging and transportation
Packaging and transportation
Quality control
 Quality objective
Quality objective
≥98 points
Job satisfaction
Customer satisfaction ≥ 98 points
≤2 pieces
Customers claim
Customer complaints ≤ 2 per month
100%
Yields
100% yield rate of finished product shipment
100%
Satisfactory rate
Main raw materials sampling inspection pass rate 100%
98%
98%
98% pass rate for rough inspection lots
≥98%
Satisfactory rate
Outside processing lot pass rate ≥98%
Performance and Parameters
Physical properties of sintered NdFeB materials
Physical properties of surface treatment and use environment
Sintered NdFeB Magnetic Properties Parameter Table
| Items | Parameter Values | Unit |
| Curie Temperature | 310~380 | ℃ |
| Relative Recoil Permeability | 1.02~1.05 | |
| Reversible Temperature Coefficient of Br (20~100℃) | -0.09~-0.13 | %/℃ |
| Reversible Temperature Coefficient of Hcj (20~100℃) | -0.4~-0.7 | %/℃ |
| Density | 7.50~7.70 | g/cm3 |
| Vickers Hardness | 550~700 | |
| Bending Strength | -0.09~-0.13 | MPa |
| Tensile Strength | ≥80 | MPa |
| Compressive Strength | 800 ~1050 | MPa |
| Electric Resistivity | 150 | μΩ·cm |
| Thermal Conductivity | 8~10 | W/(M·℃) |
| Coefficient of Thermal Expansion (Parallel to the orientation) | 5 | 10-6/K |
| Coefficient of Thermal Expansion (vertical to the orientation) | -1.5 | 10-6/K |
| Young's Modulus | 150~200 | GPa |
| (20℃~320℃)Specific Heat(20℃~320℃) | 3.0~4.6 | J/(g·k) |
| weight loss(low weight loss products) | ≤2 | mg/cm2 |
| Coating Material | Colour | Properties | Environment of Application | Thickness of Coating layer |
| Zine | Blue, Black and rainbow etc | Compact, Stable and Homogeneous | With reasonalbe capability of anticorrosion | |
| Nickel-Copper-Nickel | White and black | Light and Stable | Suitable for higher corrosive environment | |
| Phosphorization | Colorless or light gray | Uniform thickness | Short-term anticorrosion | |
| Epoxy | Black and Gray | layer with certain luster, insurability | Suitable for higher corrosive environment | |
| Parylene | Transparency | Uniform thickness, density pinholes- free and insurability | Excellent capability of anticorrosion especially for small items | |
| Ni+Cu+Epoxy | Black | Layer with certain luster insurability and stability | Excellent capability ofanticorrosion. Suitable for hostile environment salt spray resistance>300hr | |
| Al+Epoxy | Black | Layer with certain luster insurability and stability | Excellent capability of anticorrosion. Suitable for hostile environment Salt spray resistance>650hr Widely used in EV industry. |
| Grade | (Br)KGs | (Hcb)KOe | (Hcj)KOe | (BH)maxMGOe | Hk/Hcj | (T)℃ |
| N33 | 11.4~11.8 | ≥10.5 | ≥12 | 31~35 | ≥95 | 80℃ |
| N35 | 11.8-12.3 | ≥11 | ≥12 | 33~37 | ≥95 | 80℃ |
| N38 | 12.3~12.7 | ≥11.2 | ≥12 | 36~40 | ≥95 | 80℃ |
| N40 | 12.7~12.9 | ≥11.4 | ≥12 | 38~42 | ≥95 | 80℃ |
| N42 | 12.9~13.3 | ≥11.5 | ≥12 | 40~44 | ≥95 | 80℃ |
| N45 | 13.3~13.7 | ≥11.6 | ≥12 | 43~47 | ≥95 | 80℃ |
| N48 | 13.7~14.0 | ≥11.6 | ≥12 | 45~49 | ≥95 | 80℃ |
| N50 | 13.9~14.2 | ≥11.4 | ≥12 | 48~52 | ≥95 | 80℃ |
| N52 | 14.2~14.5 | ≥10.2 | ≥11 | 49~53 | ≥95 | 80℃ |
| N54 | 14.4 14.8 | ≥10.2 | ≥11 | 50~54 | ≥95 | 80℃ |
| 35M | 11.8~12.3 | ≥10.9 | ≥14 | 33~36 | ≥95 | 100℃ |
| 38M | 12.3-12.6 | ≥11.5 | ≥14 | 36~40 | ≥95 | 100℃ |
| 40M | 12.6~12.9 | ≥11.8 | ≥14 | 38~42 | ≥95 | 100℃ |
| 42M | 12.9 13.3 | ≥12.0 | ≥14 | 40~44 | ≥95 | 100℃ |
| 45M | 13.3~13.7 | ≥12.5 | ≥14 | 43~46 | ≥95 | 100℃ |
| 48M | 13.6~14.0 | ≥12.9 | ≥14 | 45~49 | ≥95 | 100℃ |
| 50M | 13.9~14.2 | ≥13 | ≥ 14 | 47~51 | ≥95 | 100℃ |
| 52M | 14.2~14.6 | ≥12.5 | ≥13 | 49~53 | ≥95 | 100℃ |
| 35H | 11.8~12.3 | ≥11 | ≥17 | 33~37 | ≥95 | 100℃ |
| 38H | 12.3~12.6 | ≥11.4 | ≥17 | 36~40 | ≥95 | 120℃ |
| 40H | 12.6~12.9 | ≥11.7 | ≥17 | 38 ~42 | ≥95 | 120℃ |
| 42H | 12.9~13.3 | ≥12.0 | ≥17 | 40 ~44 | ≥95 | 120℃ |
| 45H | 13.3~13.7 | ≥12.5 | ≥17 | 43~47 | ≥95 | 120℃ |
| 48H | 13.7~13.9 | ≥12.8 | ≥16 | 45 ~49 | ≥95 | 100℃ |
| 50H | 13.9~14.2 | ≥12.9 | ≥16 | 47~51 | ≥95 | 100℃ |
| 52H | 14.2~14.5 | ≥12.8 | ≥16 | 48 ~53 | ≥95 | 100℃ |
| 33SH | 11.4~11.9 | ≥10.5 | ≥20 | 31~35 | ≥92 | 150℃ |
| 35SH | 11.8-12.3 | ≥11.2 | ≥20 | 33~37.5 | ≥92 | 150℃ |
| 38SH | 12.3~12.6 | ≥11.3 | ≥20 | 36.5~40 | ≥92 | 150℃ |
| 40SH | 12.6~12.9 | ≥11.8 | ≥20 | 38~41 | ≥92 | 150℃ |
| 42SH | 12.9~13.3 | ≥12.4 | ≥20 | 40~44 | ≥92 | 150℃ |
| 45SH | 13.3~13.7 | ≥12.5 | ≥20 | 43~46 | ≥92 | 150℃ |
| 48SH | 13.7~14.0 | ≥12.8 | ≥20 | 45~49 | ≥92 | 150℃ |
| 50SH | 13.9~14.2 | ≥12.9 | ≥20 | 47~51 | ≥92 | 150℃ |
| 52SH | 14.2~14.5 | ≥12.8 | ≥19 | 48~53 | ≥92 | 150℃ |
| 30UH | 10.8~11.4 | ≥9.5 | ≥25 | 28~32 | ≥90 | 180℃ |
| 33UH | 11.4~11.8 | ≥10.3 | ≥25 | 31~34 | ≥90 | 180℃ |
| 35UH | 11.8~12.3 | ≥10.6 | ≥25 | 33~37 | ≥90 | 180℃ |
| 38UH | 12.3~12.6 | ≥11.1 | ≥25 | 36~39 | ≥90 | 180℃ |
| 40UH | 12.6~12.9 | ≥11.5 | ≥25 | 38~41 | ≥90 | 180℃ |
| 42UH | 12.9~13.3 | ≥11.8 | ≥25 | 40~43 | ≥90 | 180℃ |
| 45UH | 13.3~13.7 | ≥12.2 | ≥24 | 43~46 | ≥90 | 180℃ |
| 48UH | 13.7~14.2 | ≥12.5 | ≥24 | 45~49 | ≥90 | 180℃ |
| 50UH | 13.9~14.3 | ≥12.8 | ≥24 | 47~51 | ≥90 | 150℃ |
| 52UH | 14.2~14.5 | ≥13.1 | ≥24 | 48~53 | ≥90 | 180℃ |
| 30EH | 11.0~11.4 | ≥9.5 | ≥30 | 28~31 | ≥90 | 200℃ |
| 33EH | 11.4~11.8 | ≥10.3 | ≥30 | 31~34 | ≥90 | 200℃ |
| 35EH | 11.8~12.2 | ≥11.1 | ≥30 | 33~36 | ≥90 | 200℃ |
| 38EH | 12.2~12.5 | ≥11.6 | ≥30 | 35~39 | ≥90 | 200℃ |
| 40EH | 12.5~12.8 | ≥11.9 | ≥30 | 37~41 | ≥90 | 200℃ |
| 42EH | 12.8~13.1 | ≥12.2 | ≥29 | 39~43 | ≥90 | 200℃ |
| 28TH | 10.5~10.8 | ≥9.5 | ≥35 | 26~29 | ≥90 | 230℃ |
| 30TH | 10.8~11.4 | ≥10.1 | ≥35 | 28~31 | ≥90 | 230℃ |
| 33TH | 11.4~11.8 | ≥10.2 | ≥35 | 31~34 | ≥90 | 230℃ |
| 35TH | 11.8~12.2 | ≥10.6 | ≥35 | 33~36 | ≥90 | 230℃ |
| 38TH | 12.2~12.5 | ≥11.6 | ≥33 | 35~39 | ≥90 | 230℃ |
Magnetism FAQ

Neodymium Iron Magnets Coating - Parylene

Rano Magnetics: Warm Wishes for a Brilliant New Chapter

Working Principle of the Hall Element

Rano R&D of HRE-Free Magnets

Eddy Current Loss in Rare Earth Permanent Magnet Materials

Basic Concepts of Permanent Magnet Materials

NdFeB Magnets - Dimensional & Geometric Tolerances

Service Life of NdFeB—Long-Term Stability of Permanent Magnets

The difference between conventional process NdFeB magnets and cerium-containing magnets

Neodymium-Iron-Boron Surface Treatment Solution -- Passivation

Physical Properties of Sintered NdFeB Magnets

Neodymium iron boron magnet in 3C products

Magnetic Separator and Permanent Magnet
Sintered NdFeB Multi-Pole Magnetization Technology

What is the Magnetic Moment?

Orientation and Magnetization of Sintered NdFeB Magnets
The Suction Force of Magnets

Grades and Properties of Sintered NdFeB Permanent Magnets

How can You Successfully Transport Magnets by Air?

Sintered NdFeB Forming Process

Types of Permanent Magnet Materials

Temperature Stability of Permanent Magnets

Three Methods of Demagnetization

Meaning of Sintered NdFeB Grades

Heilbeck Array

Magnets in Loudspeakers

Common Plating for Magnets

Common Pre-Energy Vehicle Motors

Surface Magnetization, Remanent Magnetization and Magnetic Flux
Magnetism FAQ