The Hellebeck array is a magnet arrangement structure, and before we understand this structure, let's take a look at the distribution of magnetic lines of force for some common permanent magnets.
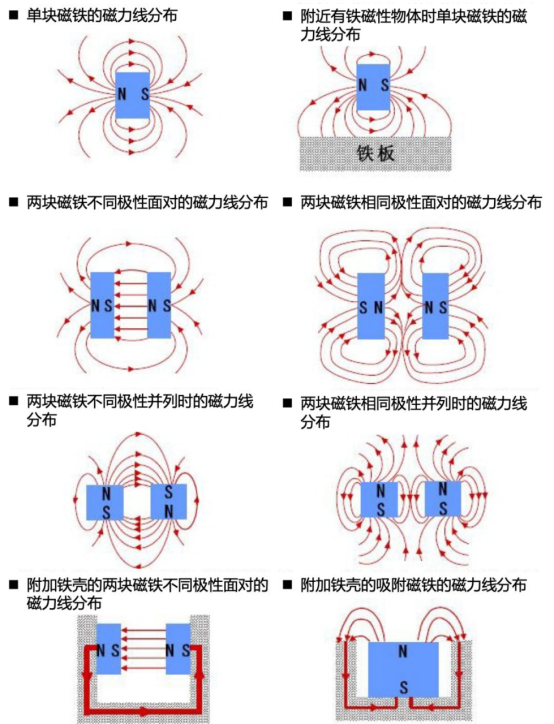
The Hellebeck array is a magnet arrangement structure, and before we understand this structure, let's take a look at the distribution of magnetic lines of force for some common permanent magnets.
Concept of the Heilbeck Array
Halbach array (Halbach Array, Halbach permanent magnet) is a kind of magnet structure, in 1979 the American scholar Klaus Halbach to do electron acceleration experiments discovered this special permanent magnet structure and gradually improved, and finally formed the so-called “Halbach” magnet. The so-called “Halbach” magnet, which is an approximate ideal structure for engineering, utilizes a special arrangement of magnet units to enhance the field strength per unit direction, with the goal of generating the strongest magnetic field with the smallest number of magnets.
The array is composed entirely of rare-earth permanent magnets, and by arranging the permanent magnets in different magnetization directions in a regular pattern, it is possible to converge the magnetic lines of force on one side of the magnet and weaken them on the other, thus obtaining a relatively ideal unilateral magnetic field. This is of great significance in engineering, and Hale-Buick arrays are widely used in industrial fields such as nuclear magnetic resonance, magnetic levitation, and permanent magnet special motors due to their excellent magnetic field distribution characteristics.
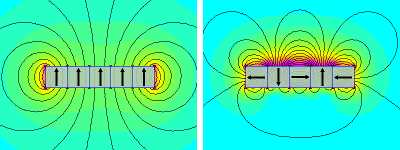
On the left is a single magnet with the north pole all the way up, and the strength of the magnetic field can be seen in the colors at the bottom and top of the magnet. On the right is a Hellebeck array with a higher magnetic field at the top of the magnet and a relatively weak one at the bottom. (The strong-side surface magnetic field strength of a Hellebeck array magnet set of the same volume is about √2 times (i.e., 1.4 times) that of a conventional single magnet, especially when the thickness of the magnet in the magnetizing direction is between 4 and 16 mm.)
Probably the most common example of a Heilbeck array has to be the flexible refrigerator sticker. These thin, flexible magnets are usually printed to be attached to refrigerators or to the back of cars, and despite their weak magnetic properties compared to NdFeB (only 2-3% strength), their low price and practicality have led to their widespread use.

Forms and Applications of the Heilbeck Array
§ Linear array
Linear is the most basic form of Halbach array composition, and this type of array magnet can be viewed as a combination of a radial array and a tangential array, as shown below. 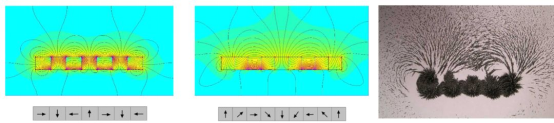
Linear Halbach arrays are currently used mainly in linear motors. The levitation principle of magnetic levitation train is that the interaction between the moving magnet and the magnetic field generated by the current it induces in the conductor produces levitation force, accompanied by magnetic resistance, and improving the ratio of buoyancy to resistance is the key to improving the performance of the levitation system, which requires light weight of the on-board magnets, strong magnetic field, uniform magnetic field, and high reliability. The Halbach array is horizontally mounted in the center of the vehicle body, which acts with the windings in the center of the track to generate the propulsion force, and maximizes the magnetic field with less magnet dosage, while the magnetic field on the other side is less, so that the passengers can avoid being exposed to the strong magnetic field.
§ Ring array
Ring Halbach arrays can be thought of as a combination of straight Halbach arrays that meet head to tail to form a circular shape.
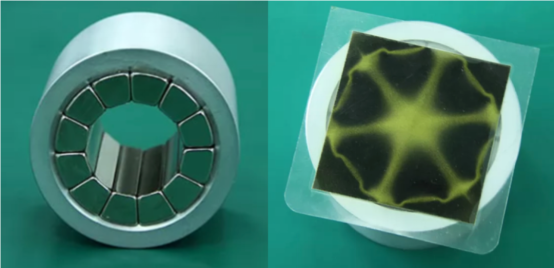
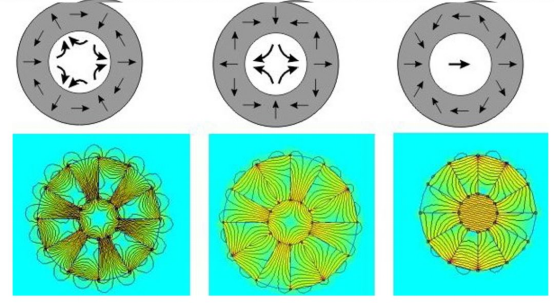
In permanent magnet motors, permanent magnet motors using Halbach array structure have air gap magnetic field closer to sinusoidal distribution than conventional permanent magnet motors, and with the same amount of permanent magnet material, Halbach permanent magnet motors have higher air gap magnetic density and lower iron loss. In addition Halbach circular arrays are widely used in permanent magnet bearings, magnetic refrigeration equipment and magnetic resonance.
Methods of fabrication and production of Halbach arrays
Method 1: According to the topology of the array, the pre-magnetized magnet segments are glued together using magnet glue. Because of the strong mutual repulsion between the magnet segments, molds are used for clamping when gluing. This method is less efficient, but easier to realize and more suitable for laboratory research.
Method 2: First use the die filling or compression molding method to create a complete magnet, and then in a special fixture for magnetization, using this method to process the array structure and the following figure is similar to this method, this method of processing efficiency, it is easier to realize the mass production. This method is highly efficient and relatively easy to achieve mass production. However, it requires a specially designed magnetizing fixture and a magnetizing process.

Method 3: Halbach-type magnetic field distribution is achieved by utilizing a specific shape of winding array as shown below.