NdFeB Magnets as Critical Components in Manufacturing
NdFeB magnets are vital parts in various manufactured products such as motors, speakers, and measuring instruments. Customers generally have specific requirements for dimensional and geometric tolerances of NdFeB magnets, as non-compliant dimensions may:
l Prevent proper installation of the magnet components
l Damage equipment due to fitting failures
l Lead to batch returns, posing significant commercial risks
Standard Tolerance Requirements
Both sintered and bonded NdFeB magnets must comply with national standards that define acceptable tolerances for:
1. Dimensional accuracy (e.g., length, width, thickness deviations)
2. Geometric precision (e.g., flatness, parallelism, circularity)
These standards serve as essential references for:
l Material selection during the design phase
l Production quality control
l Supplier evaluation
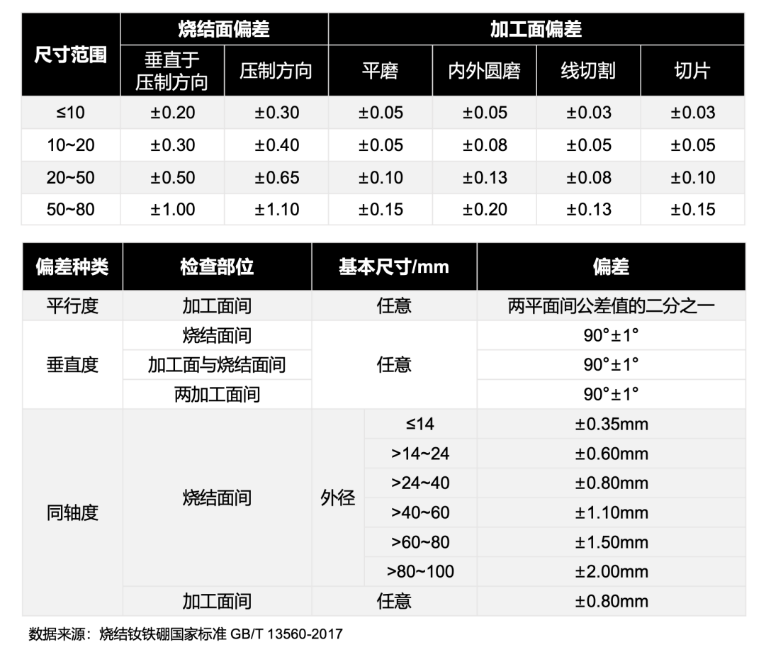
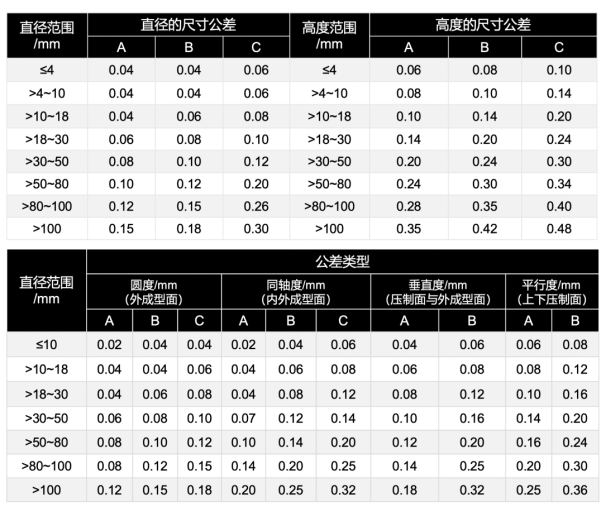
Only when both dimensional and geometric tolerance measurements meet specifications can component assembly be safe and reliable. Some manufacturers neglect geometric tolerances, resulting in assembly failures and frequent customer complaints or returns.
NdFeB magnet suppliers typically employ two inspection standards for delivery:
1. Micrometers - Only measure dimensions, cannot verify geometric tolerances
2. Go/No-Go gauges - Test both dimensions AND geometric tolerances
A common occurrence: Parts may pass micrometer inspection (dimensionally compliant) but fail Go/No-Go gauge testing. This happens because while dimensions are acceptable, geometric tolerances are non-compliant - rendering assembly impossible.

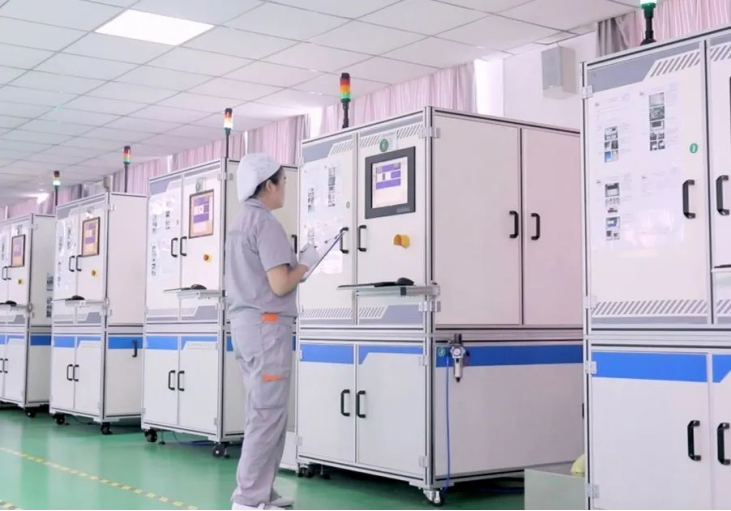
China's NdFeB magnet production has been increasing year by year. While their compact size and lightweight nature are advantageous for applications, these very features create challenges in quality inspection: the large quantity and small dimensions lead to heavy manual inspection workloads, slow detection speeds, and low accuracy. Currently, most NdFeB manufacturers primarily rely on visual manual inspection in their quality control departments, which suffers from high subjective error rates, slow processing speeds, and elevated labor costs.

The adoption of automated inspection equipment has become an industry-wide trend to overcome quality control challenges in NdFeB magnet production. With continuously increasing output volumes, many NdFeB manufacturers are now embracing innovation, progressively replacing traditional manual inspection with automated detection systems.